Restorative Medicine
Hope for Slowing ALS
Phase 1 trial uses Tregs for immunotherapy
The first-ever phase 1 clinical trial is treating ALS patients with infusions of expanded autologous regulatory T lymphocytes, or Tregs.
Since its discovery in 1869 and its rise to national attention with Lou Gehrig’s diagnosis in 1939, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS, has offered little hope for treatment. The nervous system disorder that causes the nerve cells controlling muscle movements to degenerate, inevitably leads to weakness, difficulty speaking and swallowing, impaired breathing and death, typically within three to five years.
Now, the first-ever phase 1 clinical trial for a new immunotherapy is showing surprising results, bringing hope of slowing the relentlessly progressive and fatal disease. The study, led by Houston Methodist neurologists Stanley H. Appel, MD, and Jason Thonhoff, MD, PhD, treats ALS patients with infusions of expanded autologous regulatory T lymphocytes, or Tregs. These are the immune T cells that can help protect the body from the harmful inflammation associated with the progression of ALS.
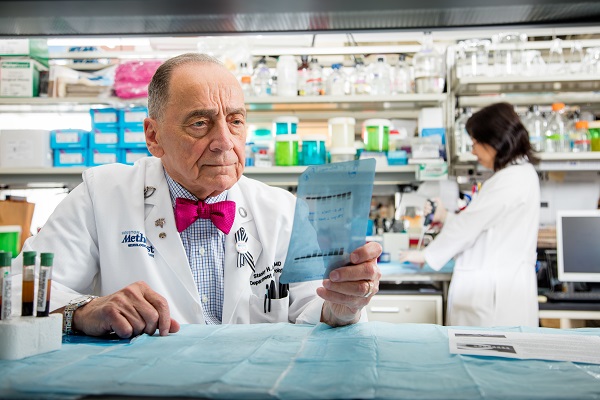

Stanley H. Appel, MD, is focusing his research on enhancing the protective immunity of Treg cells and anti-inflammatory microglia, and decreasing the proinflammatory immunity of Th1 effector lymphocytes and proinflammatory microglia.
Appel and his team selected three patients at different stages of ALS progression. Each patient underwent leukapheresis, a procedure that removed blood and separated out the white blood cells. The Tregs were then separated from the white blood cells and expanded in a specialized laboratory before being infused back into the patients. They found that Tregs that had not functioned properly when in the patient’s body, returned to normal functioning after being expanded in the lab.
We found that many of our ALS patients not only had low levels of Tregs, but also that their Tregs were not functioning properly. We believed that improving the number and function of Tregs in these patients would affect how their disease progressed.

Stanley H. Appel, MD
Peggy & Gary Edwards Distinguished Endowed Chair
Stanley H. Appel Department of Neurology
Professor of Neurology
Co-Director, Neurological Institute
Houston Methodist
Collaborating with The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Stem Cell Transplantation and Cellular Therapy program, the team collected the expanded Tregs and infused them back into the patients—and discovered that the number of Tregs increased in each patient's blood.
They gave each patient two sets of Treg infusions, with each set consisting of four infusions: The first four were administered every two weeks, and the last four each month. Disease progression appeared to slow during each set of Treg infusions according to two different rating scales of ALS progression.
“A person has approximately 150 million Tregs circulating in their blood at any given time,” said Thonhoff, the study’s lead author. “Each dose of Tregs given to the patients in this study resulted in a 30 to 40 percent increase over normal levels. Slowing of disease progression was observed during each round of four Treg infusions.”
To determine whether it is an effective treatment for slowing the progression of ALS, Appel and Thonhoff will launch a larger phase 2 study, with hope of one day developing an off-the-shelf cellular therapy for ALS patients.
Thonhoff, JR, Beers, DR, Zhao, W, Pleitez, M, Simpson, EP, Berry, JD, Cudkowicz, ME, Appel, SH. Expanded autologous regulatory T-lymphocyte infusions in ALS. Neurology® Neuroimmunology & Neuroinflammation. Jul 2018; 5 (4): 465. DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000465
This research study was approved by the Food and Drug Administration and funded by the ALS Association and ALS Finding a Cure
LaVonne Carlson, March 2019